
They commonly form near joints, such as the wrist, and can cause pain and interfere with everyday activities. Some ganglion cysts come from an injury, but most have no known cause. Your health care provider might want to monitor a lipoma through regular checkups. Usually, though, a lipoma causes no pain or other problems.

#Auditory nerve neuroma skin#
Slow-growing fat cells cause this benign, soft lump that usually appears under the skin on the neck, shoulders, back or arms. It typically causes gradually progressive weakness and loss of feeling in an arm or leg. An intraneural perineurioma happens most often in children and young adults. It may also form in soft next to a nerve, called an extraneural perineurioma. A perineurioma can form within a nerve, called an intraneural perineurioma.
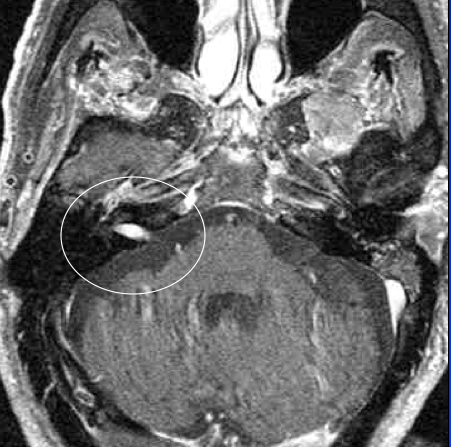
This rare benign peripheral nerve tumor arises from perineurial cells, a type of cell that surrounds the peripheral nerve sheath. People with NF1 are at risk of developing a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. These conditions include bone deformities, such as a curved spine, and an eye nerve tumor called an optic glioma. Some people who have NF1 develop other conditions. Symptoms of NF1 include color changes and benign tumors on the skin. This is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to grow on nerves. This tumor most commonly develops in people who have neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1). A neurofibroma might arise from several nerve bundles and tends to cause mild symptoms. This common type of benign nerve tumor tends to form in the center of a nerve. If acoustic neuromas aren't treated and they continue to grow, they can affect nearby nerves and press on the brainstem. It sometimes occurs in people with a condition called neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2). This type of tumor also is known as a vestibular schwannoma. This is a condition called schwannomatosis.Ī rare schwannoma near the brainstem, known as an acoustic neuroma, can cause trouble with balance or hearing. Occasionally some people have several of them in the arms, legs or body. When a schwannoma grows, more fascicles are at risk when trying to remove the tumor safely. Some schwannomas grow and form unusual shapes within the spine or pelvis, such as dumbbell tumors. But you might have a schwannoma for years before noticing it.Ī schwannoma typically comes from a single bundle of nerve fibers, called a fascicle, within the main nerve. If you develop a schwannoma in an arm or leg, you might notice a mass. These nerve sheath tumors are called schwannomas because they are made up of Schwann cells, which are cells that surround the nerves. The most common benign peripheral nerve tumor in adults, a schwannoma can occur almost anywhere on the body. Different types of benign peripheral nerve tumors include: Most are benign, meaning that they are not cancerous. The tumors that press against nerves are called extraneural tumors. Peripheral nerve tumors that grow within nerves are called intraneural tumors. Peripheral nerve tumors affect nerves by growing within them or by pressing against them.
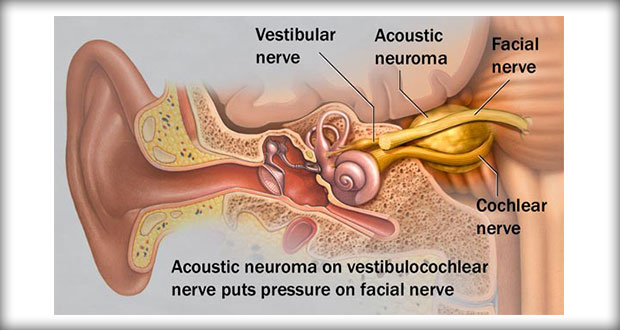

Nerve fascicles are bundles of nerve fibers. Surgeons carefully remove schwannomas while taking care to preserve nerve fascicles that aren't affected by the tumors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
